After successful local debugging, I deployed the latest code to the production environment, but I found that the chat room in the production environment could not link to my GO server’s websocket service.
Because in debug environment I use http website to connet my GO server’s websocket, but in production environment kotaku-blog.com is secure website uses https.
Chrome don’t allow insecure WebSocket connections (ws) from secure websites (https)
Although I can get around this issue during the debugging phase, the production environment has to be addressed.
I create myself SSL certification for my GO https server.
Follow this article Secure HTTPS servers in Go I start the https server in GO.
err := http.ListenAndServeTLS(":80", "cert.cer", "private.key", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("ListenAndServeTLS: ", err)
}But the browser still pops up a warning that you need to trust this certificate manually to do so.
After trust my certificate manually, I can connet to WSS websocket in https://www.kotaku-blog.com.
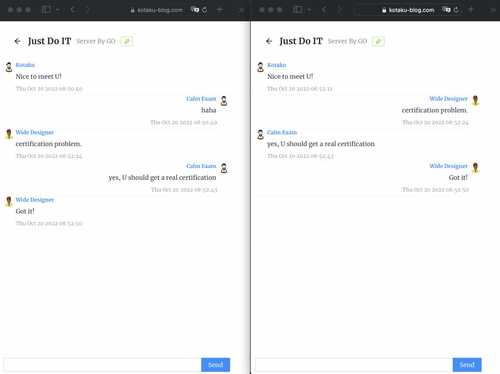
So I need a real TSL certificate for this to work.
I applied for a new domain by Router53 and applied for a certificate at AWS ACM.
But I can not download the cer and key files.
I had to add Application Load Balance (ALB) in front of the EC2 instance, which is also used to do this exactly.
You can use an HTTPS listener to offload the work of TLS encryption and decryption to your load balancer.
If you encounted the 503 service temporarily unavailable, refer to here
Remember to add a A record for you domain which route traffic to ALB.
So I just start a http GO server, it is OK.
err := http.ListenAndServe(":80", nil)